產品簡介
2.為培育在StageFlexer硅膠模表面或者基質蛋白包被的細胞培養片上的細胞提供切應力。
3.使用FX-5000T應力加載系統抻拉細胞,并且可以在實驗前,實驗中或者實驗后提供切應力
4.計算機控制蠕動泵,調節切應力大小,從0-35 dynes/cm2
5.使用標準正立式顯微鏡實時觀察細胞在切應力下的反應。
 |
世聯博研(北京)科技有限公司 |
|
—— 銷售熱線 ——
13261877206 |
Flexflow單通道平行板流室系統提供流體切應力同時抻拉細胞
1)FlexFlow顯微切應力加載設備(SHEAR Stress device)


2、流體剪切應力培養載片如下圖:

細胞培養載片包括顯微鏡載(物)片和蓋玻片兩種產品,表面經過特殊處理,適合于細胞的貼壁與生長。
兩種規格:75 mm x 25 mm x 1.0 mm ,75 mm x 24 mm x 0.2 mm 。
細胞培養載片的邊緣涂有1.0 mm寬的特氟隆邊框(Teflon),可以有效控制細胞生長在切應力加載區域。
自身熒光低,光學性能佳。
不同包被的培養表面提高細胞的貼壁與生長。
五種不同包被的培養表面:Amino, Collagen (Type I or IV) Elastin, ProNectin (RGD), Laminin (YIGSR).
所以產品都是無菌獨立包裝,僅供一次性使用。
75mm x 24mm x 0.2mm 和 FlexFlow配套使用
產品編號 英文名稱
FFCS-U Culture Slips — Untreated
FFCS-A Culture Slips — Amino
FFCS-C Culture Slips — Collagen Type I
FFCS-C(IV) Culture Slips — Collagen Type IV
FFCS-E Culture Slips — Elastin
FFCS-P Culture Slips — ProNectin
FFCS-L Culture Slips — Laminin
3)微流納流HiQ Flowmate微流體控制器




雙注射泵可以在微升、納升、微微升水平上控制液流.雙注射泵,獨立的液流控制系統。
傳送,穩定的流速
可控流速范圍1.2pL/ min-260.6ml/min
提供不同流速模型:穩定型,脈沖型,連續型,截流型和震蕩型;
可進行循環,連續的液流控制;同時運行不同的流速模型;
內置閥門控制液流模式;
機載計算器用于流量、流時、流速、剪切力的計算;
高分辨率、觸屏控制。
用戶友好的圖標驅動程序;
便于泵和芯片對接的生物芯片支架;根據現有流速有三種不同的機型;
多種應用程序:
液體稀釋,配給及注射器;
動物實驗中的藥物注射和體液抽取;
施加液流剪切力;
微流體和納流體實驗;
混合、分流液體;
震蕩型液流的控制需要iHIQ Flowmate二級閥門配件
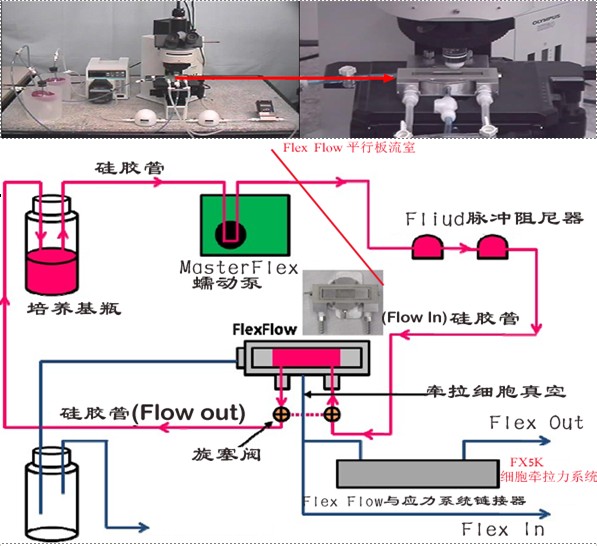
1.可以在提供流體切應力的同時抻拉細胞,測試血管和結綈組織細胞對液體流動的實時反應。
2.為培育在StageFlexer硅膠模表面或者基質蛋白包被的細胞培養片上的細胞提供切應力。
3.使用FX-5000T應力加載系統抻拉細胞,并且可以在實驗前,實驗中或者實驗后提供切應力
4.計算機控制蠕動泵,調節切應力大小,從0-35 dynes/cm2
5.使用標準正立式顯微鏡實時觀察細胞在切應力下的反應。
6.檢測細胞在流體作用下的排列反應。
7.加力同時實時檢測在液體切應力下各種激活劑/抑制劑對細胞反應的影響。使用熒光團例如FURA-2檢測細胞內[Ca2+]ic或者其它離子對切應力反應。(可以與str-4000六通道切應力系統配套使用)
FLEXFLOW AND STREAMER FLUID SHEAR STRESS SYSTEMS
1. Archambault JM, Elfervig MK, Tsuzaki M, Herzog W, Banes AJ. Shear stress response of rabbit tendon cells is serum dependent.Proceedings of the Eleventh Canadian Society for Biomechanics Conference, 181, 2000.
2. Archambault JM, Elfervig-Wall MK, Tsuzaki M, Herzog W, Banes AJ. Rabbit tendon cells produce MMP-3 in response to fluid flow without significant calcium transients. J Biomech 35(3):303-309, 2002.
3. Ge C, Song J, Chen L, Wang L, Chen Y, Liu X, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Zhang M. Atheroprotective pulsatile flow induces ubiquitin-proteasome-mediated degradation of programmed cell death 4 in endothelial cells. PLoS One 9(3):e91564, 2014. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091564. eCollection 2014.
4. Clark PR, Jensen TJ, Kluger MS, Morelock M, Hanidu A, Qi Z, Tatake RJ, Pober JS. MEK5 is activated by shear stress, activates ERK5 and induces KLF4 to modulate TNF responses in human dermal microvascular endothelial cells. Microcirculation 18(2):102-117, 2011. doi: 10.1111/j.1549-8719.2010.00071.x.
5. Eifler RL, Blough ER, Dehlin JM, Haut Donahue TL. Oscillatory fluid flow regulates glycosaminoglycan production via an intracellular calcium pathway in meniscal cells. J Orthop Res 24(3):375-384, 2006.
6. Elfervig M, Francke E, Archambault J, Herzog W, Tsuzaki M, Bynum D, Brown TD, Banes AJ. Fluid-induced shear stress activates human tendon cells to signal through multiple Ca2+ dependent pathways [abstract]. Transactions of the 46th Annual Meeting of the Orthopaedic Research Society 25:179, 2000.
7. Elfervig M, Lotano M, Tsuzaki M, Faber J, Banes A J. Fluid-induced shear stress modulates Cx-43 expression in avian tendon cells but does not induce a Ca2+ signal [abstract]. Transactions of the 47th Annual Meeting of the Orthopaedic Research Society 26:570, 2001.
8. Elfervig MK, Minchew JT, Francke E, Tsuzaki M, Banes AJ. IL-1β sensitizes intervertebral disc annulus cells to fluid-induced shear stress. J Cell Biochem 82(2):290-298, 2001.
9. Finley MJ, Rauova L, Alferiev IS, Weisel JW, Levy RJ, Stachelek SJ. Diminished adhesion and activation of plaets and neutrophils with CD47 functionalized blood contacting surfaces. Biomaterials 33(24):5803-5811, 2012. Epub 2012 May 20.
10. Francke E, Banes A, Elfervig M, Brown T, Bynum D. Fluid-induced shear stress increases [Ca2+]ic in cultured human tendon epitenon cells [abstract]. Transactions of the 46th Annual Meeting of the Orthopaedic Research Society 25:638, 2000.
11. Francke E, Elfervig MK, Sood A, Brown TD, Bynum DK, Banes AJ. Fluid-induced shear stress stimulates Ca2+ signaling in human epitenon cells [abstract]. 1999 Advances in Bioengineering, J.S. Wayne, ed. American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, 1999.
12. Gao X, Wu L, O'Neil RG. Temperature-modulated diversity of TRPV4 channel gating: activation by physical stresses and phorbol ester derivatives through protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem 278(29):27129-27137, 2003.
13. Glossop JR, Hidalgo-Bastida LA, Cartmell SH. Fluid shear stress induces differential gene expression of leukemia inhibitory factor in human mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomat Tiss Eng 1:166-176, 2011.
14. Gortazar AR, Martin-Millan M, Bravo B, Plotkin LI, Bellido T. Crosstalk between caveolin-1/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and β-catenin survival pathways in osteocyte mechanotransduction. J Biol Chem 288(12):8168-8175, 2013. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.437921. Epub 2013 Jan 28.
15. Grabias BM, Konstantopoulos K. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and fibrosis are mutually exclusive reponses in shear-activated proximal tubular epithelial cells. FASEB J 26(10):4131-41, 2012. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-207324. Epub 2012 Jun 28.
16. Hamamura K, Zhang P, Zhao L, Shim JW, Chen A, Dodge TR, Wan Q, Shih H, Na S, Lin CC, Sun HB, Yokota H. Knee loading reduces MMP13 activity in the mouse cartilage. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 14(1):312, 2013. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-14-312.
17. Hosoya T, Maruyama A, Kang MI, Kawatani Y, Shibata T, Uchida K, Warabi E, Noguchi N, Itoh K, Yamamoto M. Differential responses of the Nrf2-Keap1 system to laminar and oscillatory shear stresses in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 280(29):27244-27250, 2005.
18. Jaitovich A, Mehta S, Na N, Ciechanover A, Goldman RD, Ridge KM. Ubiquitin-proteasome-mediated degradation of keratin intermediate filaments in mechanically stimulated A549 cells. J Biol Chem 283(37):25348-25355, 2008. Epub 2008 Jul 10.
19. Kamel MA, Picconi JL, Lara-Castillo N, Johnson ML. Activation of β-catenin signaling in MLO-Y4 osteocytic cells versus 2T3 osteoblastic cells by fluid flow shear stress and PGE2: Implications for the study of mechanosensation in bone. Bone 47(5):872-881, 2010. Epub 2010 Aug 14.
20. Lee CY, Hsu HC, Zhang X, Wang DY, Luo ZP. Cyclic compression and tension regulate differently the metabolism of chondrocytes. J Musculoskeletal Res 9(2):59-64, 2005.
21. Malone AM, Batra NN, Shivaram G, Kwon RY, You L, Kim CH, Rodriguez J, Jair K, Jacobs CR. The role of actin cytoskeleton in oscillatory fluid flow-induced signaling in MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 292(5):C1830-C1836, 2007. Epub 2007 Jan 24.
22. Metaxa E, Meng H, Kaluvala SR, Szymanski MP, Paluch RA, Kolega J. Nitric oxide-dependent stimulation of endothelial cell proliferation by sustained high flow. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295(2):H736-H742, 2008. Epub 2008 Jun 13.
23. Ni J, Waldman A, Khachigian LM. c-Jun regulates shear- and injury-inducible Egr-1 expression, vein graft stenosis after autologous end-to-side transplantation in rabbits, and intimal hyperplasia in human saphenous veins. J Biol Chem 285(6):4038-4048, 2010. Epub 2009 Nov 23.
24. Qi J, Chi L, Faber J, Koller B, Banes AJ. ATP reduces gel compaction in osteoblast-populated collagen gels. J Appl Physiol 102(3):1152-60, 2007.
25. Radel C, Carlile-Klusacek M, Rizzo V. Participation of caveolae in β1 integrin-mediated mechanotransduction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 358(2):626-631, 2007. Epub 2007 May 7.
26. Radel C, Rizzo V. Integrin mechanotransduction stimulates caveolin-1 phosphorylation and recruitment of Csk to mediate actin reorganization. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288(2):H936-H945, 2005.
27. Ridge KM, Linz L, Flitney FW, Kuczmarski ER, Chou YH, Omary MB, Sznajder JI, Goldman RD. Keratin 8 phosphorylation by protein kinase C delta regulates shear stress-mediated disassembly of keratin intermediate filaments in alveolar epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 280(34):30400-30405, 2005.
28. Rosser J, Bonewald LF. Studying osteocyte function using the cell lines MLO-Y4 and MLO-A5. Methods Mol Biol 816:67-81, 2012.
29. Shim JW, Hamamura K, Chen A, Wan Q, Na S, Yokota H. Rac1 mediates load-driven attenuation of mRNA expression of nerve growth factor beta in cartilage and chondrocytes. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 13(3):372-9, 2013.
30. Sivaramakrishnan S, DeGiulio JV, Lorand L, Goldman RD, Ridge KM. Micromechanical properties of keratin intermediate filament networks. PNAS 105(3):889–894, 2008.
31. Sivaramakrishnan S, Schneider JL, Sitikov A, Goldman RD, Ridge KM. Shear stress induced reorganization of the keratin intermediate filament network requires phosphorylation by protein kinase C zeta. Mol Biol Cell 20(11):2755-2765, 2009. Epub 2009 Apr 8.
32. Srivastava T, McCarthy ET, Sharma R, Cudmore PA, Sharma M, Johnson ML, Bonewald LF. Prostaglandin E(2) is crucial in the response of podocytes to fluid flow shear stress. J Cell Commun Signal 4(2):79-90, 2010. Epub 2010 Apr 8.
33. Stachelek SJ, Alferiev I, Connolly JM, Sacks M, Hebbel RP, Bianco R, Levy RJ. Cholesterol-modified polyurethane valve cusps demonstrate blood outgrowth endothelial cell adhesion post-seeding in vitro and in vivo. Ann Thorac Surg 81(1):47-55, 2006.
34. Sun HB, Liu Y, Qian L, Yokota H. Model-based analysis of matrix metalloproteinase expression under mechanical shear. Ann Biomed Eng31(2):171-180, 2003.
35. Takai E, Landesberg R, Katz RW, Hung CT, Guo XE. Substrate modulation of osteoblast adhesion strength, focal adhesion kinase activation, and responsiveness to mechanical stimuli. Mol Cell Biomech 3(1):1-12, 2006.
36. Wang XL, Fu A, Spiro C, Lee HC. Proteomic analysis of vascular endothelial cells-effects of laminar shear stress and high glucose. J Proteomics Bioinform 2:445, 2009.
37. Wang P, Zhu F, Konstantopoulos K. The antagonistic actions of endogenous interleukin-1β and 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2 regulate the temporal synthesis of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in sheared chondrocytes. J Biol Chem 287(38):31877-93, 2012. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.362731. Epub 2012 Jul 24.
38. Wang P, Zhu F, Lee NH, Konstantopoulos K. Shear-induced interleukin-6 synthesis in chondrocytes: roles of E prostanoid (EP) 2 and EP3 in cAMP/protein kinase A- and PI3-K/Akt-dependent NF-kappaB activation. J Biol Chem 285(32):24793-24804, 2010. Epub 2010 Jun 1.
39. Wu L, Gao X, Brown RC, Heller S, O'Neil RG. Dual role of the TRPV4 channel as a sensor of flow and osmolality in renal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 293(5):F1699-F1713, 2007. Epub 2007 Aug 15.
40. Yang B, Rizzo V. Shear Stress Activates eNOS at the Endothelial Apical Surface Through β1 Containing Integrins and Caveolae. Cell Mol Bioeng 6(3):346-354, 2013.
41. Yang W, Lu Y, Kalajzic I, Guo D, Harris MA, Gluhak-Heinrich J, Kotha S, Bonewald LF, Feng JQ, Rowe DW, Turner CH, Robling AG, Harris SE. Dentin matrix protein 1 gene cis-regulation: use in osteocytes to characterize local responses to mechanical loading in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem 280(21):20680-20690, 2005.
42. Yokota H, Goldring MB, Sun HB. CITED2-mediated regulation of MMP-1 and MMP-13 in human chondrocytes under flow shear. J Biol Chem278(47):47275-47280, 2003.
43. Yoo PS, Mulkeen AL, Dardik A, Cha CH. A novel in vitro model of lymphatic metastasis from colorectal cancer. J Surg Res 143(1):94-98, 2007. Epub 2007 Jul 19.
44. Zhang K, Barragan-Adjemian C, Ye L, Kotha S, Dallas M, Lu Y, Zhao S, Harris M, Harris SE, Feng JQ, Bonewald LF. E11/gp38 selective expression in osteocytes: regulation by mechanical strain and role in dendrite elongation. Mol Cell Biol 26(12):4539-45, 2006.
45. Zhu F, Wang P, Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos A, Konstantopoulos K. Prostaglandin (PG)D(2) and 15-deoxy-Delta(12,14)-PGJ(2), but not PGE(2), mediate shear-induced chondrocyte apoptosis via protein kinase A-dependent regulation of polo-like kinases. Cell Death Differ17(8):1325-1334, 2010. Epub 2010 Feb 12.
46. Zhu F, Wang P, Lee NH, Goldring MB, Konstantopoulos K. Prolonged application of high fluid shear to chondrocytes recapitulates gene expression profiles associated with osteoarthritis. PLoS One 5(12):e15174, 2010.
FlexFlow系統包括:
FlexFlow裝置;StreamSoft軟件
FlexFlow快拆接頭、膠管、FlexFlow 旁路連接器
MASTERFLEX L/S型號7550-10蠕動泵及配套線纜、連接管
2個穩流器;硅潤滑劑
FX -5000 張力系統適配器
顯微鏡適應性FlexFlow底座
快速鏈接細胞培養基瓶;一個快速鏈接真空瓶
三個沒滅菌和六個滅菌膠原蛋白涂層薄培養載片 (載片規格:75 mm x 24 mm x 0.2 mm)
三個沒滅菌和六個滅菌膠原涂層StageFlexer膜
配件包
保證細胞在不同水平恒流或生理剪切力作用下仍保持黏附,在研究中得到了廣泛應用。用蠕動泵(peristaltic pump)或注射泵(syringe pump)提供瞬態剪切力使平行板流室的入流管和出流管之間產生壓差,使流室內細胞受到均勻,震蕩或脈動剪切力的作用
微流納流HiQ Flowmate微流體控制器
應用文獻